Zadanie Pionek [B] (pio)
Pomóż nam usprawnić bazę zadań!
Pawn [B]
Memory limit: 192 MB
The rapidly growing popularity of Bytean chess is the reason why many different
variants of this game have been invented.
Because the traditional version is played on an infinite chessboard, what
can be quite troublesome, sometimes simpler variants are chosen,
in which the dimensions of the chessboards are bounded by
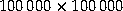 .
Some squares of the chessboard are black and the remaining ones are white,
however the painting pattern depends on the particular chessboard.
A pawn moves on such a chessboard in a bit different way than in traditional
chess - it can move horizontally, vertically or diagonally to any of the
adjacent eight squares provided that this square has the
same colour as the square currently occupied by the pawn.
.
Some squares of the chessboard are black and the remaining ones are white,
however the painting pattern depends on the particular chessboard.
A pawn moves on such a chessboard in a bit different way than in traditional
chess - it can move horizontally, vertically or diagonally to any of the
adjacent eight squares provided that this square has the
same colour as the square currently occupied by the pawn.
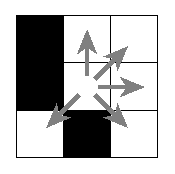
Examples of valid moves.
For given pairs of squares on the chessboard it should be determined whether a pawn can travel between these squares.
Input
The first line of the standard input contains three integers
 ,
, 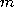 and
and 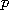 (
(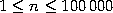 ,
, 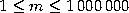 ,
,
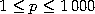 ) separated by single spaces and representing
the size of the chessboard, the number of black fragments of the chessboard
described in the input, and the number of queries, respectively.
The chessboard has dimensions
) separated by single spaces and representing
the size of the chessboard, the number of black fragments of the chessboard
described in the input, and the number of queries, respectively.
The chessboard has dimensions 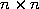 and consists of squares with both
coordinates between
and consists of squares with both
coordinates between  and
and  .
The following
.
The following 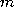 lines contain descriptions of black fragments of the
chessboard (they do not necessarily need to be disjoint).
Each one of them consists of three integers
lines contain descriptions of black fragments of the
chessboard (they do not necessarily need to be disjoint).
Each one of them consists of three integers  ,
, 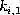 and
and 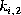 (
(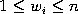 ,
, 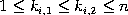 )
separated by single spaces and meaning that in row
)
separated by single spaces and meaning that in row 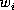 squares in
columns between
squares in
columns between 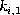 and
and 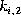 are black.
The squares that are not contained in any dark fragment specified in
the input are white.
are black.
The squares that are not contained in any dark fragment specified in
the input are white.
The following 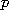 lines contain the queries.
Each query consists of two pairs of integers
lines contain the queries.
Each query consists of two pairs of integers
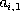 ,
, 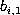 ,
, 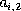 ,
, 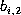 (
(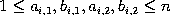 )
separated by single spaces.
The query is: can a pawn get from the square in row
)
separated by single spaces.
The query is: can a pawn get from the square in row 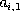 and column
and column 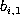 to the square in row
to the square in row 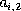 and column
and column
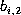 ?
?
Output
Your program should output  lines to the standard output:
the answers to the respective queries, in the same order as they
appear in the input.
The answer to each query is a line with a word "TAK"
(meaning YES) or "NIE" (meaning NO) without the quotes,
depending on whether a pawn can get from the first of the specified squares
to the second one without passing through a square with different colour.
lines to the standard output:
the answers to the respective queries, in the same order as they
appear in the input.
The answer to each query is a line with a word "TAK"
(meaning YES) or "NIE" (meaning NO) without the quotes,
depending on whether a pawn can get from the first of the specified squares
to the second one without passing through a square with different colour.
Example
For the input data:
4 5 2 1 1 1 2 3 4 3 2 2 4 2 2 4 2 2 1 1 3 2 1 2 4 4
the correct result is:
NIE TAK
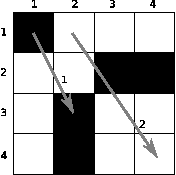
The chessboard and the queries from the example.
Task author: Krzysztof Diks.
Kontakt
In the event of technical difficulties with Szkopuł, please contact us via email at [email protected].
If you would like to talk about tasks, solutions or technical problems, please visit our Discord servers. They are moderated by the community, but members of the support team are also active there.

 English
English